
The Candida Diet: A Holistic Approach to Reclaiming Your Health
The Candida diet has gained popularity in recent years as an effective means to combat Candida overgrowth, a condition caused by an imbalance of yeast in the body.
By following a structured eating plan, individuals can restore balance to their gut flora and alleviate a range of symptoms associated with Candida overgrowth.
In this article, we will delve into the details of the Candida diet, exploring its benefits, guidelines, and the science behind its effectiveness.
Understanding Candida Overgrowth:
Candida overgrowth occurs when the natural balance of microorganisms in the body, particularly the gut, is disrupted. Candida albicans, a common type of yeast, can multiply excessively, leading to a myriad of health issues such as fatigue, digestive problems, skin irritations, and mood swings. The Candida diet aims to starve the yeast and restore a healthy equilibrium.
The Basics of the Candida Diet:
The Candida diet involves eliminating certain foods that promote yeast growth while focusing on those that support a healthy digestive system. Here are the key guidelines to follow:

Say No to Sugar:
Sugar acts as fuel for Candida, encouraging its growth and multiplication. Hence, the diet emphasizes the reduction or elimination of refined sugars, artificial sweeteners, and high-glycemic fruits from the menu. Instead, natural sweeteners like stevia can be used in moderation.
Embrace Wholesome Foods:
Whole foods, such as vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, form the foundation of the Candida diet. These nutrient-dense choices provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants to strengthen the immune system and support overall well-being.
Limit Carbohydrates:
While complex carbohydrates like whole grains and legumes are generally healthy, they can still contribute to Candida overgrowth if consumed excessively. The diet suggests moderate consumption of these foods and encourages a focus on low-glycemic alternatives such as quinoa, buckwheat, and amaranth.
Probiotics and Fermented Foods:
To restore a healthy balance of gut bacteria, the Candida diet promotes the consumption of probiotics and fermented foods. These include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and other fermented vegetables. Probiotics help crowd out Candida, promoting a diverse and beneficial microbial environment.
Benefits of the Candida Diet:
The Candida diet offers a range of potential benefits for individuals struggling with Candida overgrowth. By following this eating plan, individuals may experience:
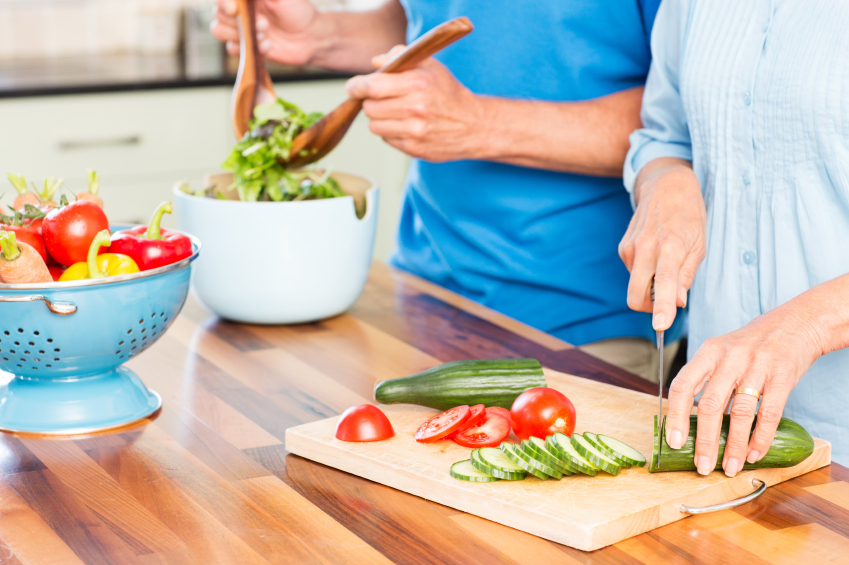

Improved Digestive Health:
Eliminating foods that contribute to gut inflammation and encouraging the consumption of gut-friendly foods can lead to improved digestion and reduced symptoms such as bloating and gas.
Enhanced Energy Levels:
As Candida overgrowth can cause fatigue and lethargy, adopting the Candida diet may lead to increased energy levels and improved overall vitality.
Balanced Mood and Mental Clarity:
The gut and brain are intricately connected through the gut-brain axis. By rebalancing gut health, the Candida diet may support mental well-being, potentially alleviating symptoms of brain fog and mood swings.
Strengthened Immune System:
A healthy gut microbiome plays a crucial role in supporting a robust immune system. By fostering a diverse and balanced microbial environment, the Candida diet may enhance immune function and reduce the frequency of infections.
Supporting Detoxification: An Essential Component of the Candida Diet
Detoxification plays a vital role in the Candida diet, aiding in the elimination of toxins released during the die-off process. By including detoxifying foods and practices, individuals can enhance the effectiveness of the diet and support their body’s natural cleansing mechanisms.
Some beneficial strategies include increasing water intake, consuming detoxifying herbs like milk thistle and dandelion root, incorporating foods rich in antioxidants such as berries and leafy greens, and practicing techniques like dry brushing and saunas to promote sweating and toxin elimination.
Navigating Social Situations: Maintaining the Candida Diet Outside Your Home
Following the Candida diet can present challenges when dining out or attending social gatherings. However, with a little planning and preparation, it is possible to stick to the diet while still enjoying social interactions.

Strategies include researching restaurant menus in advance, opting for grilled or steamed protein and vegetable dishes, bringing a dish to share at potlucks that aligns with the Candida diet, and communicating your dietary needs with friends and family to ensure they understand and can accommodate your requirements.
The Importance of Lifestyle Factors: Stress Management and Quality Sleep
While diet plays a central role in combating Candida overgrowth, lifestyle factors should not be overlooked. Chronic stress and poor sleep can weaken the immune system and disrupt the delicate balance of gut flora, potentially exacerbating Candida overgrowth.
Incorporating stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels.
Additionally, prioritizing quality sleep by establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing sleep environment can contribute to overall well-being and support the effectiveness of the Candida diet.
Conclusion:
The Candida diet offers a holistic approach to addressing Candida overgrowth, focusing on dietary modifications to rebalance gut health and improve overall well-being.
By adhering to the guidelines and making thoughtful food choices, individuals can take control of their health and reclaim vitality. However, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before embarking on any significant dietary changes.
FAQ:
Q1: Can I still enjoy desserts while following the Candida diet?
While the Candida diet restricts the consumption of refined sugars and high-glycemic fruits, there are still options to satisfy your sweet tooth.
Some alternatives include using natural sweeteners like stevia or monk fruit in moderation, experimenting with sugar-free recipes that use ingredients such as coconut flour or almond flour, and incorporating small amounts of low-glycemic fruits like berries into your diet
Q2: How long should I follow the Candida diet?
The duration of the Candida diet varies from person to person and depends on the severity of Candida overgrowth and individual response to the dietary changes.
While some individuals may experience improvements within a few weeks, others may need to follow the diet for several months. It’s recommended to work closely with a healthcare professional who can monitor your progress and provide guidance on the duration of the diet based on your specific circumstances.
Q3 Are there any potential side effects of the Candida diet?
As the Candida diet involves significant dietary changes, some individuals may experience temporary side effects during the initial stages. These can include headaches, fatigue, and mild digestive discomfort as the body adjusts to the new eating plan. These symptoms typically subside within a few days or weeks.
Q4: Can I reintroduce restricted foods after following the Candida diet?
Once you’ve successfully completed the Candida diet and achieved a healthier balance in your gut flora, it may be possible to reintroduce certain foods that were previously restricted.
However, it’s crucial to do this gradually and observe how your body reacts to each food. Some individuals may find that certain foods still trigger symptoms of Candida overgrowth, while others may be able to enjoy a wider variety of foods without adverse effects.
Also Read:
You May Also Like

Understanding /8sza1ucqrs4 & its Usage Unlocking the Potential In 2023
May 12, 2023
Easy Access to Your Favorite Shows with hbomax/tvsignin enter code:
April 8, 2024

